Complete Guide to Kubernetes Management: Best Practices and Cost Optimization
Kubernetes makes deploying containerized applications straightforward—until the cluster grows and the monthly cloud bill arrives. What starts as a simple orchestration platform quickly becomes a complex environment requiring deliberate management practices to keep costs under control and operations running smoothly.
This guide covers the core components of Kubernetes clusters, proven management best practices, cost optimization strategies, and the tools that help teams maintain visibility and efficiency across their environments.
What is Kubernetes Management
Kubernetes management refers to the processes, tools, and practices used to deploy, maintain, secure, and optimize containerized workloads running on Kubernetes clusters. This includes automating deployments, implementing security controls, monitoring cluster health, and controlling costs.
At its core, effective Kubernetes management brings together infrastructure provisioning, application deployment, security governance, and financial oversight into a unified approach.

Organizations running containerized applications rely on Kubernetes management to keep their environments stable, secure, and cost-efficient. Without deliberate management practices, clusters tend to become difficult to maintain and expensive to operate over time.
Why Kubernetes Management Matters
Kubernetes environments grow complex quickly. Teams often find themselves troubleshooting unexpected outages, addressing security gaps, or facing surprisingly high cloud bills at the end of each month.
Structured management approaches help organizations avoid these pitfalls by delivering:
- Operational efficiency: Automation reduces manual work and human error
- Cost control: Proper resource allocation prevents waste and overspending
- Security compliance: Governance frameworks help maintain regulatory standards
- Scalability: Well-managed clusters support growth without performance issues
Understanding Kubernetes Clusters
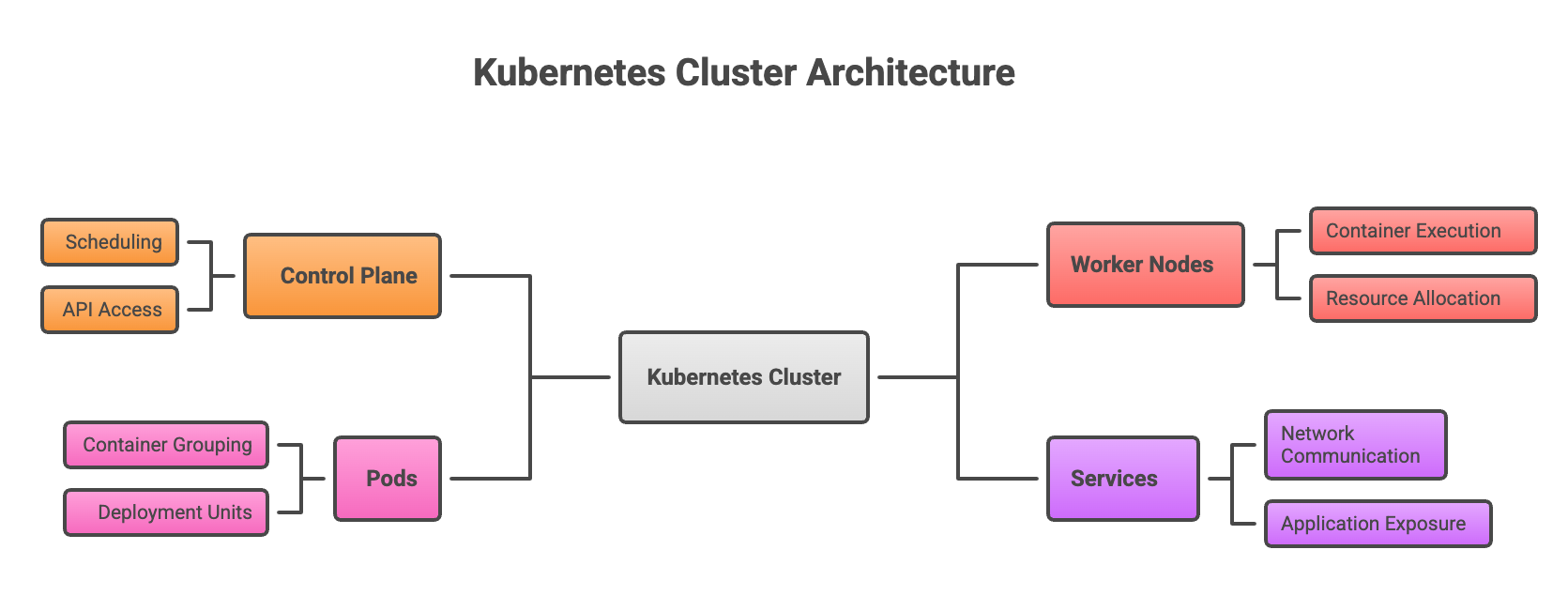
A Kubernetes cluster is a set of machines, called nodes, that work together to run containerized applications. The control plane manages the overall cluster state by making scheduling decisions and responding to events like a pod failing or a new deployment request. Worker nodes provide the actual compute capacity where applications run.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Control Plane | Manages cluster state, scheduling, and API access |
| Worker Nodes | Run containerized application workloads |
| Pods | Smallest deployable units containing one or more containers |
| Services | Expose applications and enable network communication |
Understanding this architecture makes it easier to reason about resource allocation, security boundaries, and scaling decisions.
Best Practices for Kubernetes Management
1. Implement Role-Based Access Control
Role-Based Access Control, or RBAC, is a security mechanism that limits who can access what within a cluster based on their role in the organization. Rather than giving everyone administrative access, RBAC allows you to define specific permissions for different user groups.
For example, a developer might have permission to deploy applications in a test namespace, while only platform engineers can modify production configurations. This principle of least privilege reduces the risk of accidental or malicious changes to critical systems.
2. Configure Resource Requests and Limits
Every container in Kubernetes can specify resource requests and limits. Requests represent the minimum CPU and memory a container requires to run, while limits define the maximum resources it can consume. Setting these values properly prevents one application from using all available resources and starving other workloads.
Without defined requests and limits, a single misbehaving application can consume an entire node's resources and cause widespread disruption.
3. Use Namespaces for Multi-Tenancy
Namespaces are logical partitions within a single Kubernetes cluster. They allow different teams or applications to coexist without interfering with each other. Organizations commonly create separate namespaces for development, staging, and production environments, each with its own resource quotas and access policies.
This separation makes it easier to manage permissions, track resource usage, and prevent configuration conflicts between teams.
4. Enable Autoscaling for Dynamic Workloads
Kubernetes offers three complementary autoscaling mechanisms that work together to match infrastructure to actual workload demands:
- Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA): Adds or removes pod replicas based on CPU, memory, or custom metrics
- Vertical Pod Autoscaler (VPA): Adjusts CPU and memory requests for individual pods based on observed usage
- Cluster Autoscaler: Adds or removes worker nodes when pods cannot be scheduled due to insufficient capacity
When configured properly, these tools prevent both under-provisioning during traffic spikes and waste during quiet periods.
5. Establish Monitoring and Observability
Visibility into cluster health, application performance, and resource utilization is essential for proactive management. Centralized monitoring using tools like Prometheus for metrics collection and Grafana for visualization helps teams identify problems before they affect users.
Observability goes beyond simple monitoring by providing the context needed to understand why something is happening, not just that it is happening.
6. Adopt GitOps for Version Control
GitOps is an approach that treats infrastructure configuration as code, storing it in Git repositories and using automated pipelines to apply changes. Tools like Flux CD and Argo CD continuously compare the desired state defined in Git with the actual cluster state and reconcile any differences.
This approach provides audit trails for every change, enables quick rollbacks when problems occur, and ensures consistency across multiple environments.
7. Plan for Backup and Disaster Recovery
Clusters fail. Regions go offline. Human errors happen. Regular backups of cluster state, persistent volumes, and application data—combined with tested recovery procedures—protect organizations from catastrophic data loss.
Tools like Velero can automate backup and restore operations across clusters, making it practical to maintain recovery capabilities without significant manual effort.
What is the Most Effective Way to Manage Kubernetes Costs
The most effective approach combines visibility, rightsizing, automation, and governance. Organizations that excel at cost management typically start by understanding where money is actually going, then systematically eliminate waste.
Key tactics include:
- Rightsizing resources: Matching CPU and memory allocation to actual usage patterns rather than developer estimates
- Leveraging spot instances: Using discounted compute capacity for workloads that can tolerate interruption
- Implementing cost allocation: Tagging resources to attribute spending to specific teams or projects
- Automating optimization: Deploying tools that continuously adjust resources based on demand
Kubernetes Cost Allocation Strategies
Tracking costs in Kubernetes requires deliberate effort because resources are shared and dynamic. Organizations use labels and annotations on Kubernetes objects to attribute spending to specific teams, applications, or cost centers.
Two common models exist for cost attribution. Showback provides visibility into what each team is spending without actual financial consequences. Chargeback goes further by actually billing internal teams for their resource consumption. Both approaches encourage accountability and cost-conscious decision-making among engineering teams.
Common Kubernetes Cost Challenges
Even well-intentioned teams struggle with Kubernetes costs for several reasons:
- Lack of visibility: Traditional cloud billing does not map cleanly to Kubernetes resources, making it hard to see where money goes
- Overprovisioning: Developers often request more resources than applications actually use, creating persistent waste
- Idle resources: Development and staging environments frequently run around the clock even when no one is working
- Multi-cloud complexity: Managing costs across different providers with different pricing models adds significant overhead
These challenges compound over time, often resulting in cloud bills that grow faster than the business value being delivered.
Top Kubernetes Cost Management Solutions
1. Kubecost
Kubecost provides real-time cost visibility and optimization recommendations for Kubernetes environments. The open-source version offers basic monitoring capabilities, while enterprise tiers add features like multi-cluster support and advanced allocation reporting.
2. Karpenter
Karpenter is an AWS-native node provisioner that automatically selects the most cost-effective instance types for workloads. It responds to pending pods within seconds, making it particularly effective for variable workloads that scale frequently.
3. Spot by NetApp
Spot by NetApp is a multi-cloud optimization platform that automates spot instance management across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. It handles the complexity of spot instance interruptions and replacement automatically.
4. OpenCost
OpenCost is a CNCF sandbox project providing vendor-neutral cost monitoring. As an open-source foundation, it integrates with various platforms and avoids lock-in to any specific vendor ecosystem.
5. Cloud Provider Native Tools
AWS Cost Explorer, Google Cloud Cost Management, and Azure Cost Management offer built-in cost analysis capabilities. While less Kubernetes-specific than dedicated tools, they provide valuable context about overall cloud spending.
| Tool | Best For | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|
| Kubecost | Detailed cost visibility | Freemium |
| Karpenter | AWS node optimization | Open-source |
| OpenCost | Vendor-neutral monitoring | Open-source |
| Spot by NetApp | Multi-cloud spot management | Commercial |
Essential Tools for Managing Kubernetes Clusters
1. kubectl and CLI Tools
kubectl is the command-line interface for interacting with Kubernetes clusters. Every administrator uses it daily for deployments, troubleshooting, and cluster inspection. Tools like k9s add terminal-based visual interfaces that make navigation faster and more intuitive.
2. Helm for Package Management
Helm is a package manager for Kubernetes that bundles applications into reusable "charts" defining all necessary resources. Rather than managing dozens of individual YAML files, teams can deploy complex applications with a single command and customize them through values files.
3. Prometheus and Grafana for Monitoring
This combination has become the standard for Kubernetes observability. Prometheus scrapes and stores metrics from applications and infrastructure, while Grafana transforms that data into actionable dashboards and alerts. Together, they provide the visibility teams rely on for day-to-day operations.
5. Managed Kubernetes Services
Amazon EKS, Azure AKS, and Google GKE handle control plane management, upgrades, and availability on behalf of their customers. These services reduce operational burden significantly, though they come with their own pricing considerations and feature differences worth evaluating.
How to Choose a Kubernetes Cost Management Tool
Selecting the right tool depends on your specific environment and requirements. Consider these factors when evaluating options:
- Integration requirements: Compatibility with existing monitoring, CI/CD, and infrastructure tools
- Multi-cloud support: Whether the tool can manage costs across multiple cloud providers
- Automation capabilities: The level of autonomous optimization available
- Reporting features: Ability to generate allocation reports for finance and leadership teams
- Total cost of ownership: What the tool itself costs relative to expected savings
Building a Kubernetes Cost Optimization Strategy
Kubernetes costs grow fast when teams lack visibility. Engineers often make decisions without knowing the financial impact, and leadership struggles to hold anyone accountable for cloud overspend.
Real progress starts with clear visibility, followed by setting targets and tracking results. This turns cost control from a one-time effort into an ongoing practice.
Obsium helps teams fix the common pain points that drive waste: unclear ownership, inefficient cluster design, overprovisioned workloads, and limited insight into where money is actually going. With expert guidance and Kubernetes-focused services, Obsium improves performance, streamlines operations, and brings spending under control.
See how Obsium can help you reduce waste, strengthen governance, and run Kubernetes with confidence.
FAQs about Kubernetes Management and Cost Optimization
What is the difference between Kubernetes cost management and cost monitoring?
Cost monitoring provides visibility into spending patterns and trends. Cost management goes further by encompassing active optimization efforts, governance policies, budget controls, and allocation practices that actually reduce expenses over time.
Can Kubernetes cost management tools work across multiple cloud providers?
Many tools support multi-cloud environments, though capabilities vary significantly. Cloud-native tools like AWS Cost Explorer only cover their own platform, while solutions like Kubecost and OpenCost offer vendor-neutral monitoring across providers.
How do organizations allocate Kubernetes costs to specific teams or projects?
Organizations apply consistent labels and annotations to Kubernetes resources, then use cost allocation tools to aggregate spending by those labels. This data feeds into showback reports or chargeback systems that assign financial responsibility to specific cost centers.
What causes unexpected Kubernetes cost increases?
Common causes include overprovisioned resources that never get rightsized, autoscaling configurations that scale up but fail to scale down, idle development environments, excessive data transfer between availability zones, and limited visibility into namespace-level spending.
Ready to Get Started?
Let's take your observability strategy to the next level with Obsium.
Contact Us