Availability Zones
An availability zone, or AZ, is an isolated physical data center within a cloud region. Each zone operates with its own power, networking, and cooling infrastructure, allowing applications to remain available even if one zone experiences an outage. Availability zones are a core building block for highly reliable and fault tolerant cloud systems.
Understanding Availability Zones
Availability zones are separate data centers located within the same geographic region. They are designed to work together while remaining independent, so a failure in one zone does not cascade to others.
What Makes an Availability Zone Independent
Each availability zone includes its own:
- Independent power and backup generators
- Dedicated cooling systems
- Separate network infrastructure
- Physical and operational security
This isolation protects applications from common failures such as hardware issues, power outages, or localized disasters.
Availability Zones Within a Region
A cloud region is made up of multiple availability zones connected by fast, low latency networks.
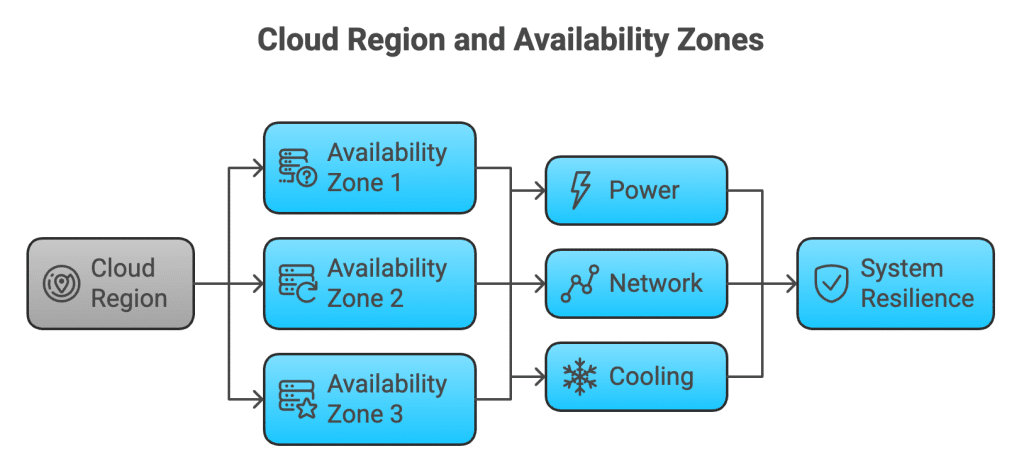
By spreading workloads across zones within a region, systems can continue operating even when one zone becomes unavailable.
Role in Distributed Databases
Availability zones are especially important for distributed databases and time series platforms, where uptime and data durability are critical.
Data Replication Across Zones
- Data is copied across multiple availability zones
- Ensures data remains accessible if a zone fails
- Reduces the risk of permanent data loss
Failover and Resilience
- Traffic automatically shifts to healthy zones
- Applications remain responsive during failures
- Downtime is minimized without manual intervention
This architecture is commonly used in financial systems, monitoring platforms, and industrial workloads.
Implementation Consideration
Designing systems across availability zones involves several important tradeoffs.
1. Latency and Performance
- Cross zone communication introduces small delays
- Replication can impact write performance
- Read operations are often served from the nearest zone
2. Cost Management
- Data transfer between zones may increase costs
- Resources should be evenly distributed
- Backup and recovery plans must consider zone placement
3. Consistency Models
- Strong consistency across zones can affect throughput
- Eventual consistency may offer better performance
- Zone placement influences quorum based systems
Best Practices for Using Availability Zones
1. Zone Distribution
- Deploy across at least three availability zones
- Avoid single zone dependencies
- Balance compute and traffic across zones
2. Monitoring and Automation
- Continuously monitor zone health
- Automate failover and recovery processes
- Track cross zone performance metrics
3. Data Protection
- Use zone aware replication strategies
- Maintain backups across zones
- Regularly test recovery procedures
Ready to Get Started?
Let's take your observability strategy to the next level with Obsium.
Contact Us